You can contact to me using this form.
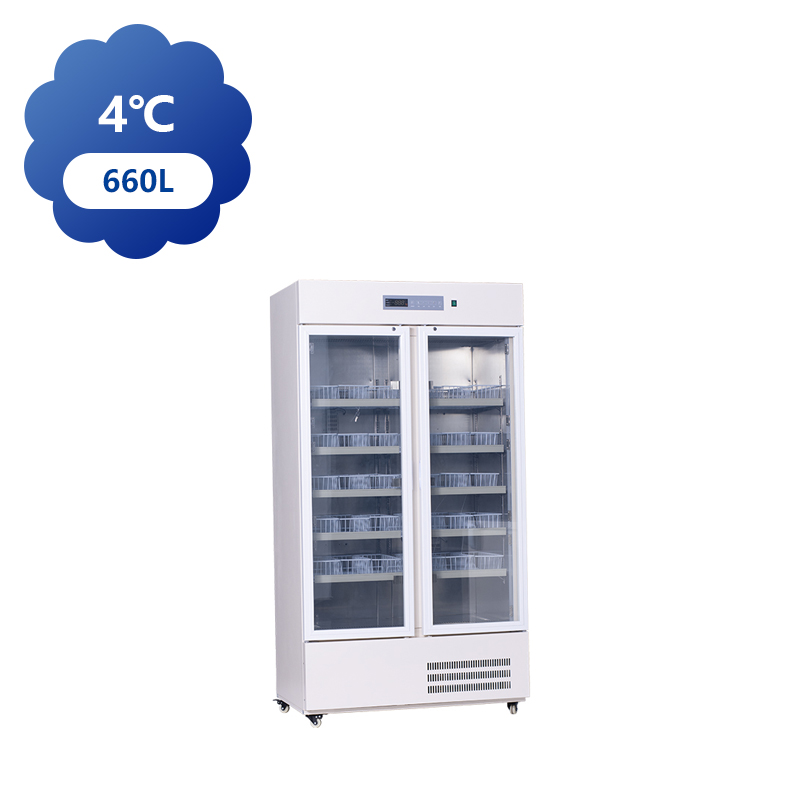
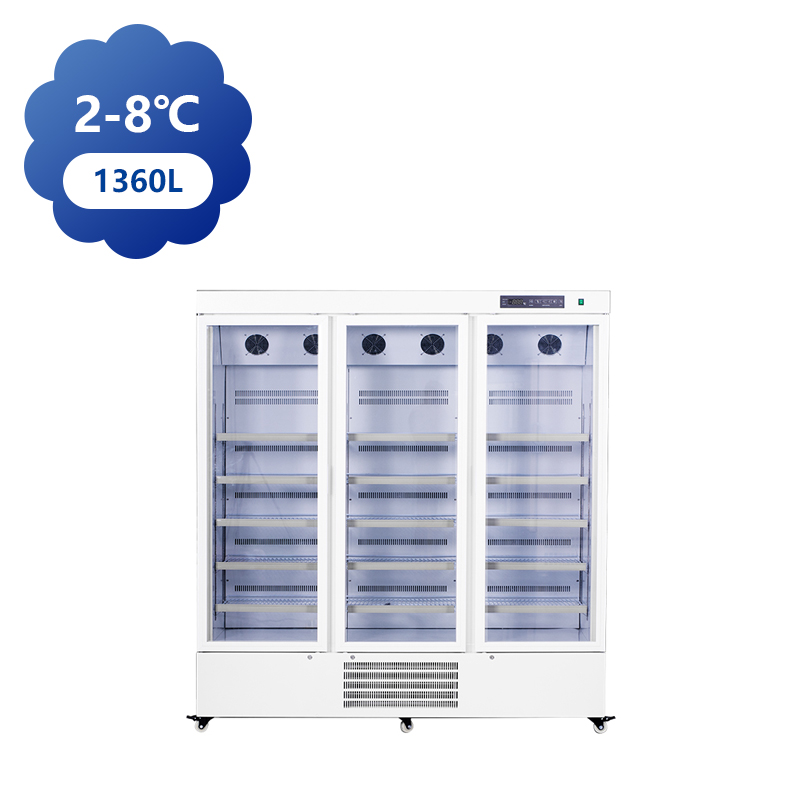
The production of Blood Bank Fridge is a highly specialized process that ensures medical-grade refrigeration systems are capable of storing blood and blood products at precise temperatures. These units must meet stringent standards set by healthcare organizations and regulatory bodies. The production process is a combination of advanced engineering, quality control, and regulatory compliance, ensuring that blood is stored safely and remains viable for use in transfusions and other medical procedures.

The production begins with the design phase, where manufacturers focus on the specific requirements of blood storage, such as temperature consistency, capacity, and reliability. Blood bank refrigerators are designed to operate at temperatures typically ranging from 1°C to 6°C for whole blood and red blood cells, while plasma may require different storage conditions. In this phase, engineers focus on ensuring that the refrigerator is equipped with the necessary cooling components to achieve these temperatures while maintaining efficiency.
Once the design is finalized, the manufacturing phase begins. The step is the construction of the refrigerator's frame, which is typically made from stainless steel for durability and hygiene. This frame is then insulated with high-quality materials to maintain the required temperature. Insulation materials, such as polyurethane foam or polystyrene, are carefully selected for their thermal properties to prevent heat exchange with the environment.
Next, the cooling system is installed. Blood bank fridges use a refrigeration cycle involving compressors, evaporators, and condensers to maintain the desired temperature. The refrigeration system is carefully calibrated and tested to ensure it operates within the precise temperature range. Digital temperature controllers are also integrated into the system to monitor and regulate temperature, providing real-time data to hospital staff.
Once the cooling system is in place, the refrigerator's interior is configured for storage. Adjustable shelves, compartments, and dividers are installed to accommodate various types of blood products, allowing for efficient organization. Each compartment is designed to ensure proper air circulation around the stored blood, preventing the risk of temperature variation and ensuring that blood is preserved in the possible condition.
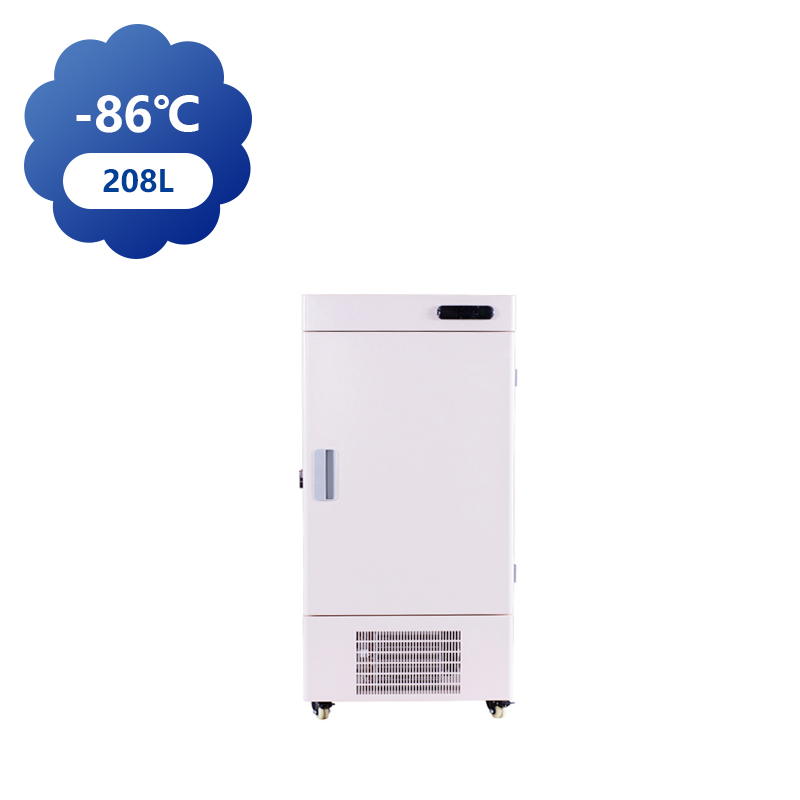
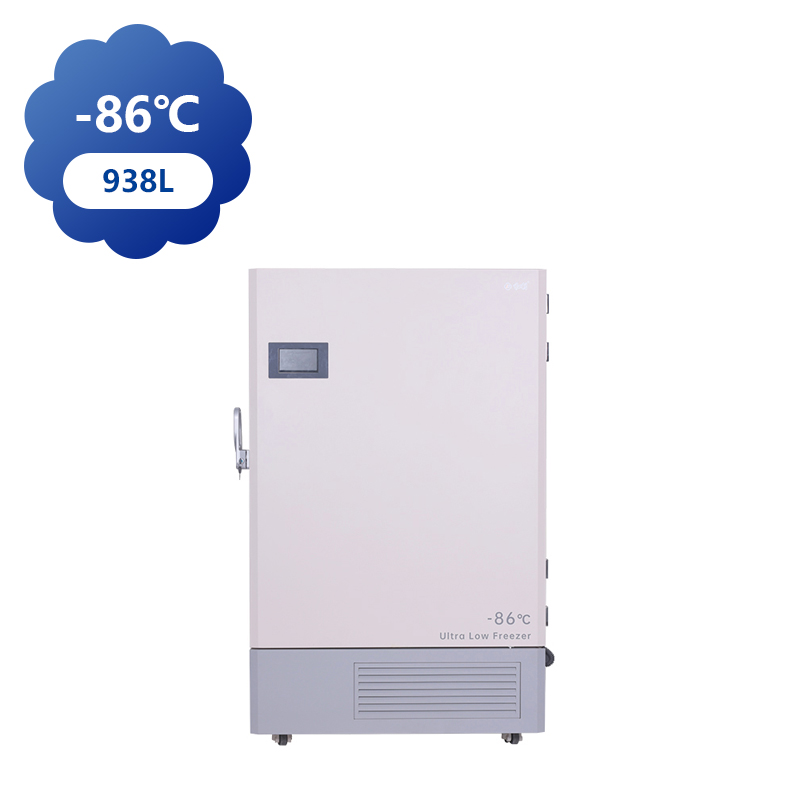
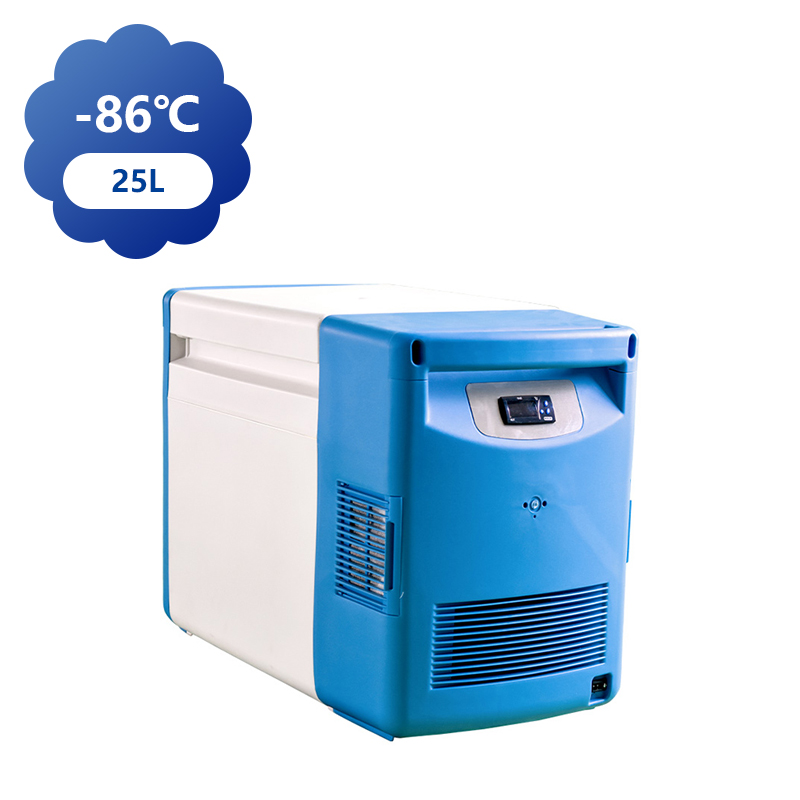
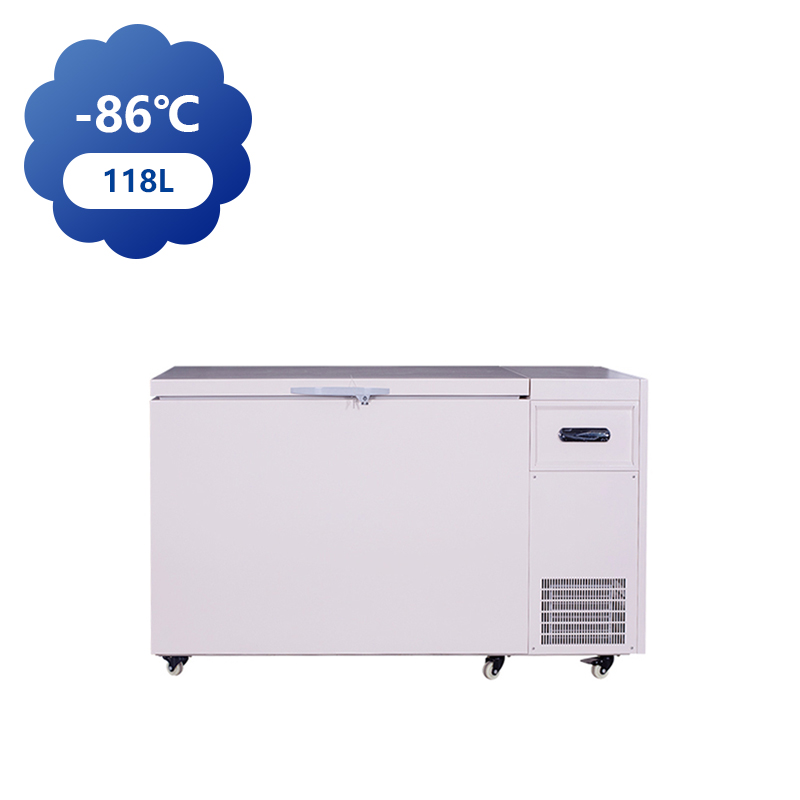
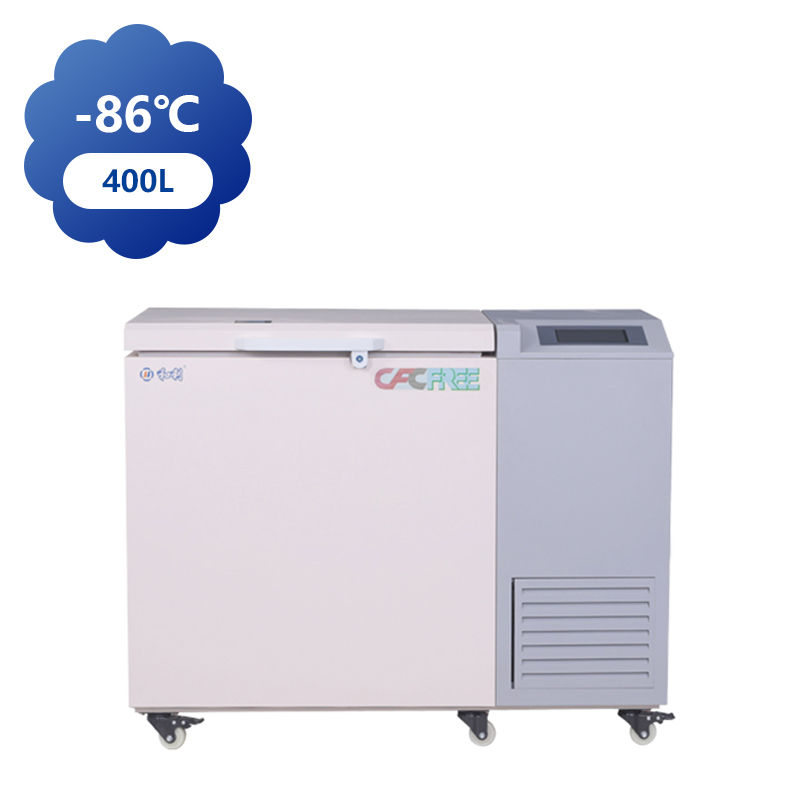
Ultra-low temperature freezers, capable of reaching temperatures as low as -80°C, have a broad range of applications across various industries, particularly in healthcare, scientific research, and biotechnology. These freezers are essential for preserving sensitive materials that require storage in cold conditions, and their use is growing due to advances in medicine, biotechnology, and environmental research.
In the medical field, ultra-low temperature freezers are indispensable for storing vaccines, biological samples, and other medical products that must remain stable at sub-zero temperatures. Vaccines, particularly those for diseases like COVID-19, often require storage at temperatures well below freezing to preserve their efficacy. These freezers offer an ideal solution, as they can store large quantities of vaccines and other biological products for extended periods without compromising their quality.
Beyond vaccines, ultra-low temperature freezers are also used in blood banks and clinical laboratories to store blood, plasma, and other biological materials. These freezers help ensure that blood products remain viable for transfusions, while biological samples used in research can be preserved for future study. In research settings, ultra-low temperatures prevent the degradation of delicate materials, such as proteins, enzymes, and DNA, allowing scientists to preserve samples for long-term analysis.
In biotechnology, ultra-low temperature freezers are used to store cell cultures, tissue samples, and reagents, ensuring that they remain in condition for experimental use. Researchers rely on these freezers to maintain the integrity of samples used in drug development, genetic research, and clinical trials. In many cases, ultra-low temperature storage is a requirement for regulatory compliance, ensuring that research is conducted under the controlled conditions.
Additionally, ultra-low temperature freezers are used in the field of environmental science. These freezers are employed to preserve soil, water, and air samples collected from various environmental studies, ensuring that they remain unchanged until they can be analyzed. This is particularly important in long-term environmental monitoring, where scientists need to track changes in ecosystems over extended periods.


 中文简体
中文简体 English
English Français
Français عربى
عربى +86-15988502726(wechat)
+86-15988502726(wechat)